Effective Strategies for Dealing with Stress in Daily Life
Understanding Stress and Its Impact
What is Stress?
Stress is a natural response of the body to perceived threats or challenges, often referred to as “stressors.” It triggers a series of emotional and physical reactions, commonly known as the “fight or flight” response. Stress can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild irritation to overwhelming anxiety. Knowing how to manage stress effectively is crucial for maintaining both mental and physical health. Many individuals find themselves needing support in dealing with stress, particularly in high-pressure environments.
Common Causes of Stress
Stress can arise from numerous sources, and understanding these can help individuals take proactive steps to mitigate its effects. Common causes include:
- Work Pressure: Job-related demands and deadlines can overwhelm employees, leading to significant stress.
- Financial Concerns: Uncertainty about finances, bills, and economic fluctuations can heavily contribute to stress levels.
- Relationship Issues: Conflicts with friends, family, or romantic partners can be emotionally taxing and stressful.
- Health Problems: Personal health issues or the health of loved ones can create worry and anxiety.
- Major Life Changes: Events such as moving, divorce, or job loss can lead to significant stress as individuals adapt to new situations.
Physical and Mental Effects of Stress
The impact of stress is not limited to emotional challenges; it can also lead to physical symptoms, including:
- Headaches: Chronic stress can lead to tension headaches.
- Digestive Issues: Stress can exacerbate conditions like irritable bowel syndrome or lead to changes in appetite.
- Sleep Disturbances: Anxiety may result in difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Increased Heart Rate: Stress can elevate heart rate and blood pressure.
- Immunity Issues: Prolonged stress can weaken the immune system, making one more susceptible to infections.
Techniques for Dealing with Stress
Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
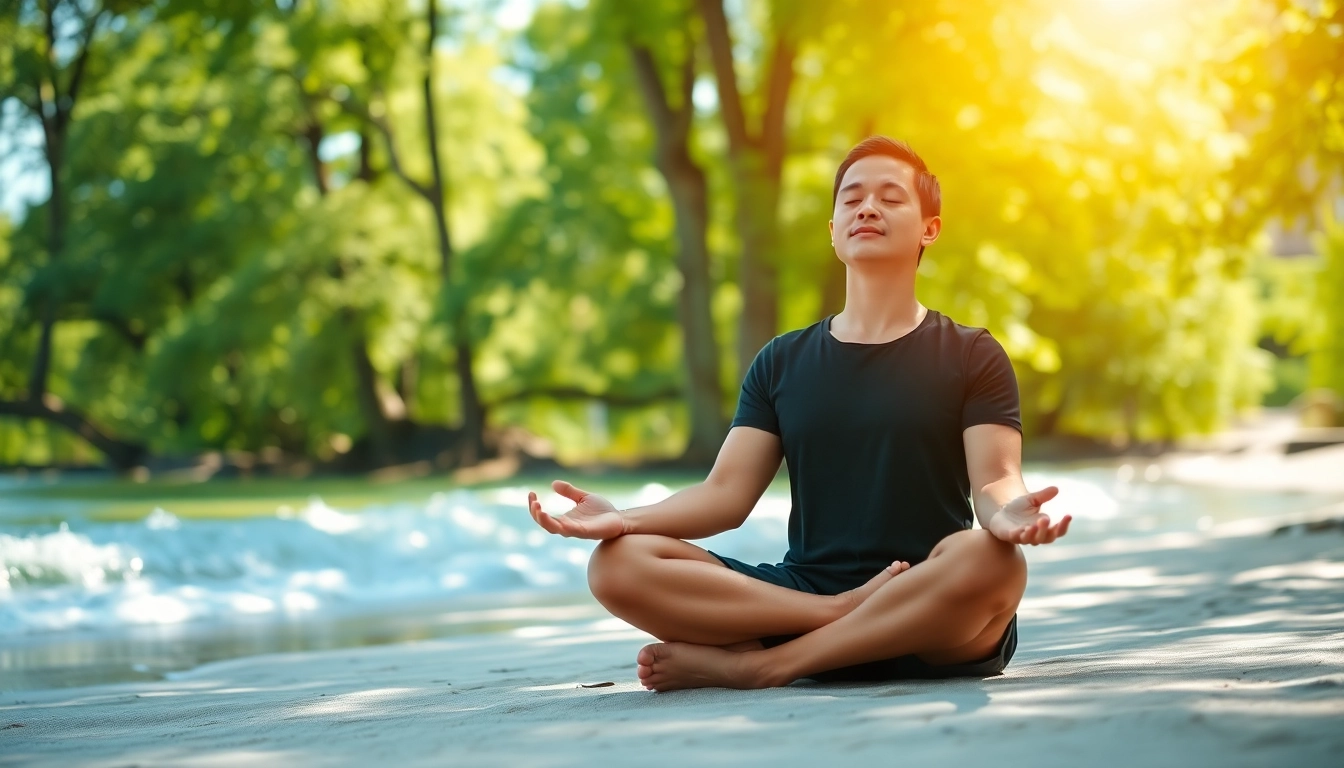
Mindfulness and meditation are powerful tools in managing stress. These practices help individuals focus on the present moment, allowing them to detach from stressful thoughts and emotions. Techniques may include:
- Deep Breathing: Taking slow, deep breaths helps calm the nervous system.
- Guided Meditation: Using apps or videos to follow meditation sessions can provide structure to practice.
- Body Scanning: Focusing attention on different parts of the body helps release physical tension.
Physical Activities to Relieve Stress
Physical activity is an effective means to reduce stress levels. Exercise releases endorphins, leading to a feeling of well-being. Types of effective activities include:
- Aerobic Exercises: Running, cycling, or dancing can energize and uplift mood.
- Yoga: Combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to alleviate stress.
- Walking: A simple and accessible way to clear the mind and enjoy the outdoors.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits not only enhances well-being but also assists in dealing with stress. Beneficial choices include:
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a wide range of nutrients can bolster mood and energy levels.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water is crucial for overall health and can improve mental clarity.
- Sleep Hygiene: Creating a relaxing bedtime routine helps ensure quality sleep.
Building a Support System
The Importance of Social Connections
Strong social connections can act as buffers against stress. Engaging with friends, family, or support groups provides comfort and understanding. It’s essential to foster relationships that offer mutual support and shared experiences.
Communicating Your Feelings
Articulating feelings and thoughts is vital for emotional health. Open communication can prevent feelings of isolation. Techniques to improve communication include:
- Active Listening: Prioritize understanding others while expressing your thoughts.
- Sharing Coping Strategies: Discussing what works in reducing stress can benefit all parties involved.
- Seeking Feedback: Encourage others to share their perspectives, which may reveal new approaches to managing stress.
Seeking Professional Help
Sometimes, stress may feel unmanageable, and seeking professional help can be crucial. Therapists and counselors can provide therapeutic strategies tailored to individual experiences. Common forms of therapy beneficial for stress management include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): Combines meditation and yoga to address stress.
- Support Groups: Engaging with individuals experiencing similar issues can provide comfort and shared insights.
Creating a Stress-Resilient Environment
Organizing Your Space
Clutter can exacerbate stress. Organizing physical spaces can help create a calming environment that supports mental clarity. Consider these steps:
- Declutter Regularly: Spend a few minutes each day sorting and organizing.
- Create Dedicated Workspaces: Separating work from personal space can enhance focus and relaxation.
- Incorporate Plants: Greenery can create a soothing atmosphere and improve air quality.
Time Management Strategies
Effective time management is a cornerstone of stress reduction. Here are several techniques to consider:
- Prioritize Tasks: Use tools like to-do lists to identify high-priority activities.
- Set Boundaries: Learn to say no when commitments become overwhelming.
- Break Projects into Steps: Dividing tasks into manageable segments can reduce feelings of being overwhelmed.
Incorporating Relaxation Zones
Creating designated relaxation zones in your space can promote downtime. This could be a meditation nook, a hammock in the yard, or simply a cozy chair by the window. Key elements to include:
- Comfortable Seating: Ensure that your relaxation space is inviting and comfortable.
- Sensory Elements: Add candles, soft music, or essential oils to create a calming atmosphere.
- Distraction-Free Area: Design the space to minimize interruptions from technology and daily stressors.
Monitoring and Evaluating Stress Levels
Recognizing Signs of Stress
Awareness is the first step in managing stress. Recognizing early signs can help you take action before stress escalates. Common signals include:
- Changes in Mood: Increased irritability or a sense of hopelessness can indicate rising stress levels.
- Physical Symptoms: Look out for headaches, stomach issues, or fatigue.
- Behavioral Changes: Notice alterations in sleep patterns or eating habits.
Journaling for Self-Reflection
Keeping a journal can be an effective way to process thoughts and emotions. Journaling serves various purposes:
- Tracking Stressors: Documenting experiences helps identify patterns and triggers.
- Clarifying Emotions: Writing can provide insight into feelings and responses.
- Generating Gratitude: Focusing on positive experiences can balance the influence of stressors.
Adjusting Techniques for Continuous Improvement
Managing stress is an ongoing process that requires regular evaluation. It’s important to adapt strategies based on personal effectiveness. Consider these practices:
- Set Goals: Create specific, achievable goals for stress management.
- Periodic Reflection: Regularly assess which stress-reducing techniques are effective and adjust as needed.
- Seek Feedback: Don’t hesitate to ask trusted individuals about their perspective on your stress management approaches.